Bloomberg News
Powell Signals No Rush to Cut Interest Rates Further

[Stay on top of transportation news: Get TTNews in your inbox.]
U.S. Treasuries held small losses after Federal Reserve Chair Jerome Powell affirmed that the central bank favors delaying additional interest-rate cuts.
“We know that reducing policy restraint too fast or too much could hinder progress on inflation,” Powell said in prepared testimony for the Senate Banking Committee. His remarks echoed the message he delivered Jan. 29, when the Fed paused after cutting rates three times last year.
Treasury yields, already higher by as much as four basis points before Powell’s first day of congressional testimony began at around 10 a.m., remained near those levels. The U.S. 10-year year climbed nearly five basis points toward 4.55%, extending its rebound from last week’s 2025 low of 4.38%. A gauge of the dollar held steady after two days of gains.
“The Fed is on pause until future notice,” said George Catrambone, head of fixed income at DWS Americas. “Powell still has trouble publicly reconciling their pause with his confidence in overall policy restrictiveness. He won’t be able to do that dance forever, especially in the back half of this year if inflation hasn’t come down further.”
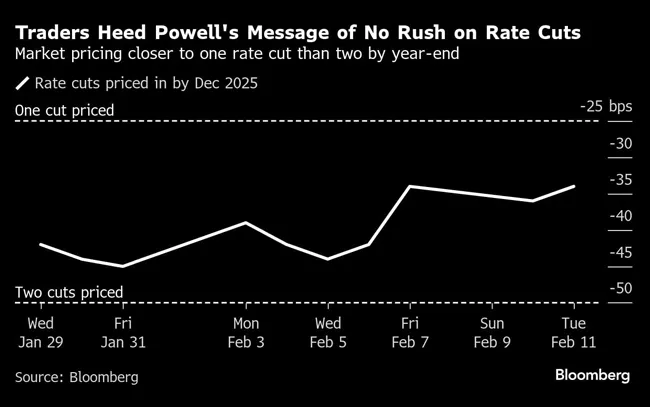
(Bloomberg)
Money markets continued to fully price in just one quarter-point rate cut by the central bank this year, by September. In December, two 2025 cuts were priced in. A strong January jobs report released Feb. 7 prompted reassessment of the policy outlook, and January inflation data to be released Feb. 12 could do the same.
Speaking earlier Feb. 11, Cleveland Fed President Beth Hammack said it’s appropriate to keep interest rates steady for “some time” while policymakers await further downward progress on inflation and analyze the economic effects of new government policies.
RELATED: Fed Sees Risks 'in Balance' as It Holds Rates at 4.25%-4.5%
Longer-maturity Treasury yields have climbed since U.S. President Donald Trump was elected in November, partially on speculation that the trade protectionism he campaigned on could prove inflationary.
At the same time, administration officials have said they want lower yields on 10-year Treasuries — which are set by the market and reflect expectations for growth and inflation — and aren’t seeking cuts to the overnight interest rate set by the Fed.
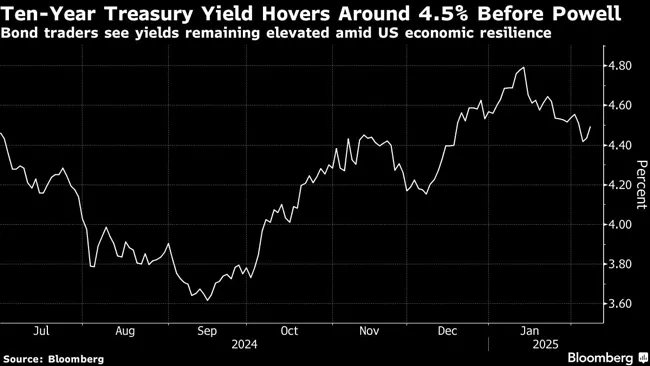
(Bloomberg)
The 10-year yield climbed to around 5% in 2023, the highest level in 15 years, amid a surge in inflation, and has remained above 3.6% since then.
“If the administration seeks lower 10-year yields they should focus less on tariffs and more on fiscal policy,” Catrambone said. He expects the 10-year to remain in a 4.25% to 4.75% range.
The rise in yields, if sustained, will mean higher returns for buyers of this week’s three Treasury note and bond auctions, including the Feb. 11 $58 billion of three-year notes followed by 10- and 30-year issues over the next two days.
Demand was strong for the three-year notes, which were awarded at 4.300%, lower than their 4.313% yield in pre-auction trading just before the bidding deadline.
The 10.2% share awarded to primary dealers was the lowest on record in data that go back to 2004, another sign of strong demand from investors. The indicated yield for the auction had been as low as 4.18% since it was announced last week.
Want more news? Listen to today's daily briefing below or go here for more info:




