Bloomberg News
Biden’s Infrastructure Plan Endangered by Dire Shortages

[Stay on top of transportation news: Get TTNews in your inbox.]
The biggest threat to President Joe Biden’s vision of energizing the U.S. economy with the largest infrastructure program in decades may not be its challenging path through Congress, but a dire shortage of everything from workers to cement mills.
While weeks or months of negotiations will be needed to enact legislation, Republicans and Democrats are united in their support for hundreds of billions of dollars in new spending on infrastructure in coming years. Yet the companies that will be relied on to pave the roads, build the bridges, lay the water pipes and assemble the trains aren’t yet planning to meet those needs, economists and industry insiders say.
And that’s even as they face immediate shortages — from steel and cement to the supply of labor — stemming from the unprecedented difficulties of a sudden reopening of the economy after last year’s shutdowns.
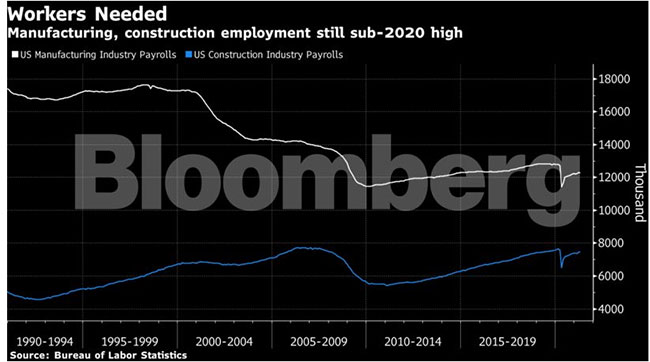
“There’s already a labor shortage in construction, so you can’t throw a trillion-dollar nuclear bomb of money into the industry,” said Bassem Hamdy, CEO of Briq, a company that runs cost estimates for construction firms. “If you don’t have workers, how will this ever happen?”
Construction firms still are excited for more busines but aren’t taking steps to boost hiring or move workers in anticipation of the package passing, Hamdy said. U.S. steelmakers aren’t boosting supply enough to meet expected demand. And tariffs on items including aluminum and lumber are hampering affordability.
The scarcities have caught the attention of the White House. Biden, touting his infrastructure plan during a visit to Cleveland last week, said his administration “will take steps to combat these supply pressures, starting with the construction materials and transportation bottlenecks,” with plans to be unveiled in coming days.
For all the “Made in America” push by both Biden and his predecessor, Donald Trump, American manufacturers are confronted with a legacy of historically mediocre growth over the past decade, and a future colored by lackluster U.S. demographic trends. These factors alone discourage companies from ramping up capacity, even amid dizzying prices.
Consider steel, the price of which has skyrocketed about 225% to $1,665 a ton in the year to May 31. Biden’s legislation would increase demand for the material by 5% each year in the first five years of an infrastructure plan, or about 5 million tons per year, according to CRU Group, a commodities research firm.
Planned capacity coming online by the end of 2022 is only about 4.6 million tons a year, according to Bloomberg Intelligence analyst Andrew Cosgrove. That would squeeze prices and supply even more.
The American Jobs Plan will rebuild our nation’s crumbling infrastructure and help tackle the climate crisis head-on. Watch as Ali Zaidi, White House Deputy National Climate Advisor, explains more in 15 seconds or less. pic.twitter.com/z0ms7VelNh — President Biden (@POTUS) June 3, 2021
Yet U.S. Steel Corp., the country’s oldest maker of the metal, is pulling back on investing in its plants.
CEO David Burritt told shareholders in April he would be scrapping a more than $1 billion plan to rehabilitate a Pittsburgh steelmaking plant that dates to Andrew Carnegie. The company has no plans to restart blast furnaces that it shuttered in 2020. Steel for infrastructure projects accounts for less than 1% of U.S. Steel’s annual revenue, according to data compiled by Bloomberg.”
Over at Charlotte, N.C.-based Nucor Corp., rather than unveiling preparations for new mills, the company last month authorized a $3 billion stock buyback plan.
Nucor said in a statement, “We are poised and ready to do our part to help rebuild our nation’s infrastructure,” and listed $4.24 billion of investments over the past three years to modernize and expand the company’s production capability and product portfolio.
Even so, U.S. producers are so overbooked on orders that American consumers are forced to rely on foreign steel, despite the holdover tariffs from the Trump administration.
Tom Conway, president of United Steelworkers, the largest industrial union in North America, said he’s concerned that the supply crunch means the infrastructure push will have to source materials abroad, benefiting other countries with employment gains, instead of the U.S.
“Here’s what I think the administration has to be concerned about,” Conway said. “They’re going to press and press and press trying to get an infrastructure bill and all these manufacturers will say, ‘We’re not ready. We need more runway to get ready. So in the meantime, get it offshore and do the projects and we’ll get started on ours.’ ”
The housing industry, which has boomed thanks to low mortgage rates, is worried about the competition coming from infrastructure projects. The National Association of Home Builders says the U.S. will need to lift tariffs on lumber and import more key metals to ensure there’s enough aluminum for appliances, copper for wiring and cement for foundations.
Domestic U.S. saw mills haven’t kept up with construction, and the housing industry imports about 30% of its lumber from Canada. Lumber prices are up an estimated 400% since the start of the 2020 recession.
The infrastructure bill “will place a huge demand for steel and concrete that will impede our ability to build out multifamily and other types of housing,” said Jerry Howard, CEO of NAHB. “You’ve got to increase output. And where that’s going to come from? Lord only knows. It’ll be difficult to enact because of the lack of supplies, labor, everything.”
One constant shortage cited across the country is people. The infrastructure bill increases the demand for trained workers, which the U.S. doesn’t necessarily have. The manufacturing industry remains down more than 500,000 positions from February 2020. Immigration could help, but that’s politically challenging.
“By the time we get to infrastructure hitting the ground, there will be a labor shortage and to some extent the government is going to have to compete with private businesses for people,” said Aneta Markowska, chief U.S. economist at Jefferies.
Delays in passing the infrastructure bill may end up being beneficial, according to Michael Gapen, chief U.S. economist at Barclays Plc. Constraints on supply chains could ease over time, he said.
“If you pass infrastructure too soon and we’re trying to source all these goods, we’re just going to ramp up existing frictions in markets,” Gapen said. “But most people believe an infrastructure bill won’t go into effect until next year.”
Want more news? Listen to today's daily briefing below or go here for more info:




